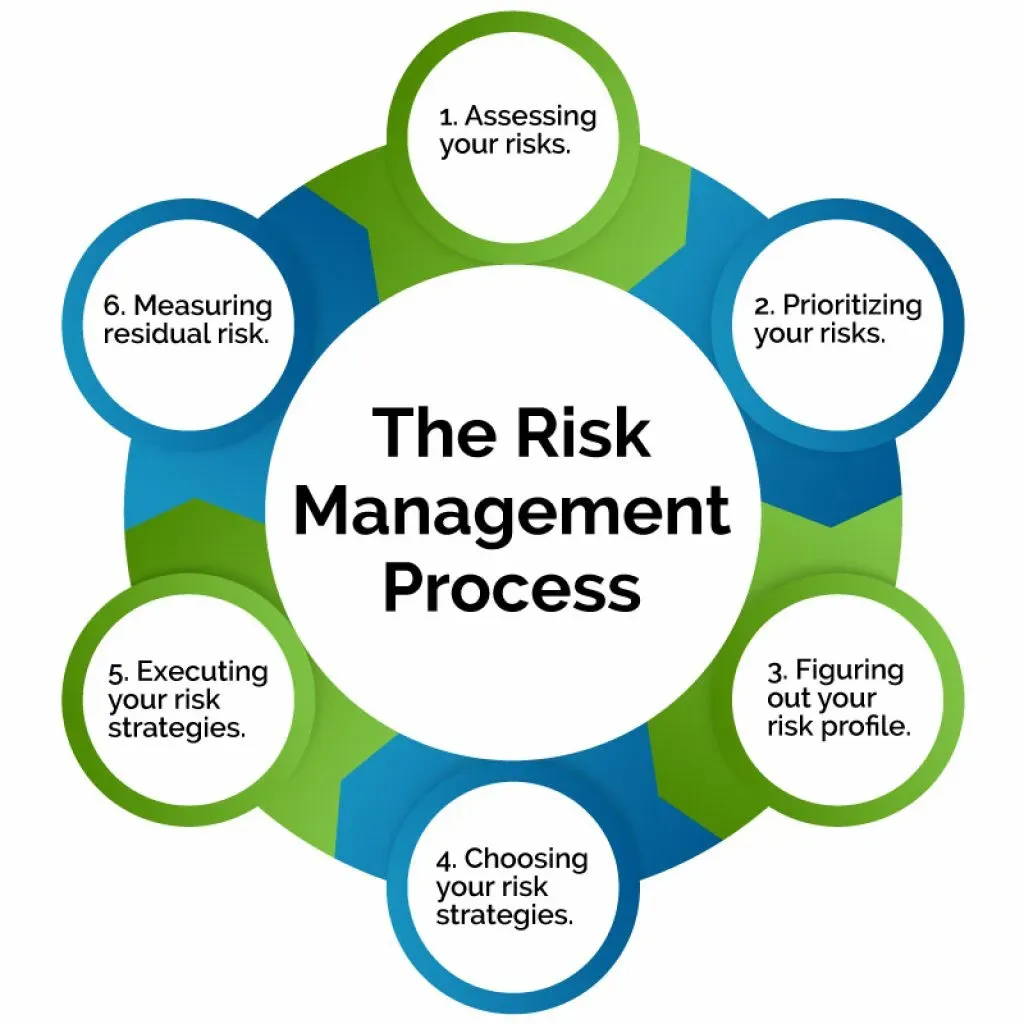
Risk management in business is not about eliminating every risk; it’s about spotting what could go wrong, weighing how likely and how damaging those events would be, and applying deliberate strategies to reduce impact while preserving opportunity. In a world of rapid change, uncertainty is a constant that leaders must acknowledge rather than ignore. By weaving risk mitigation strategies into planning and operations, organizations build resilience and clearer priorities. A strong program helps teams anticipate disruptions, protect critical assets, and make smarter decisions under pressure. With measurable steps and ongoing governance, prudent risk practices can turn threat into opportunity and support sustainable growth.
Viewed through the lens of enterprise risk management, organizations frame threats as interconnected pressures on strategy, operations, and finance rather than isolated incidents. This approach emphasizes risk governance, alignment of decision rights, accountability, and transparent reporting to leaders. A practical starting point is a formal risk assessment that informs where to concentrate resources, how to diversify exposure, and when to build buffers. By embracing a strategic risk planning mindset, teams embed uncertainty-aware processes into product design, supplier management, and capital decisions, strengthening resilience across the value chain.
Risk management in business: Integrating enterprise risk management and risk assessment for resilience
Risk management in business is a strategic capability that goes beyond checking boxes. It requires identifying threats, evaluating how likely they are to occur, and judging the potential damage they could cause to objectives such as revenue, operations, and reputation. By aligning with enterprise risk management (ERM) principles and applying risk assessment in business, leaders can map risk to strategy, establish clear ownership, and set a credible risk appetite. Frameworks like ISO 31000 and COSO help organize this work, but the real value comes from integrating risk thinking into planning, product development, and governance.
With a practical program, teams move from analysis to action. They implement risk mitigation strategies, embed monitoring dashboards, and weave risk data into decision making. Operational risk management practices come into play in daily processes, supplier choices, and technology use, ensuring controls are tested, incidents are detected early, and contingency plans are ready. A robust risk governance structure—clear accountability, cross‑functional collaboration, and a culture that speaks openly about risk—turns insights into resilient performance and value preservation.
Operational risk management and practical risk mitigation strategies for sustainable growth
Operational risk management drives resilience in daily operations. It focuses on processes, people, systems, and facilities, and uses risk mitigation strategies such as controls, scenario planning, redundancy, and incident response to prevent disruptions from becoming costly events. By connecting day‑to‑day risk management with enterprise‑level oversight, organizations can improve supply chain reliability, protect data integrity, and strengthen continuity planning. In this view, risk becomes a continuous feedback loop rather than a one‑off exercise.
Measuring success requires clear indicators and disciplined risk assessment in business practice. Leading indicators—incident frequency, near misses, mean time to detect—complement lagging metrics like loss exposure and recovery time. Regular risk reporting, governance reviews, and ongoing training ensure teams stay aligned with the risk appetite while pursuing growth. Over time, the combination of operational risk management, risk mitigation strategies, and continuous improvement creates a durable foundation for sustainable growth and stakeholder confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is risk management in business and how does enterprise risk management enhance resilience?
Risk management in business is a systematic, ongoing process to identify, assess, treat, monitor, and communicate risks that could affect objectives. When aligned with enterprise risk management (ERM), it connects risk appetite to strategy, assigns clear ownership, and implements controls. This integrated approach helps organizations anticipate disruptions, protect key assets, reduce losses, and pursue opportunities with greater confidence.
What are practical risk mitigation strategies within risk assessment in business to safeguard operations and performance?
A practical set of risk mitigation strategies includes: strengthen governance and accountability; diversify and secure the supply chain; invest in resilience and continuity planning; improve data governance and cybersecurity; use scenario planning and stress testing; strengthen financial controls and liquidity management; embrace risk transfer mechanisms; and foster a culture of learning and transparency. Where possible, link these actions to operational risk management to prevent disruptions and improve decision speed during crises.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Definition of risk management in business |
|
| Why it matters |
|
| Core components |
|
| Frameworks & standards |
|
| Implementation steps |
|
| Practical strategies |
|
| Operational risk management in daily practice |
Operational risk management is the day-to-day muscle of risk governance. It focuses on processes, people, technology, and facilities that enable the business to run smoothly. It designs controls to prevent errors, detects anomalies early, and creates resilient processes that adapt during disruptions. It requires leadership and collaborative problem-solving, with operations teams involved from the outset for early risk detection, better quality, and smoother execution. |
| Example |
A mid-size manufacturing company facing supply chain volatility and rising energy costs builds a risk profile (supplier concentration, energy price risk, compliance exposure), maps controls (dual sourcing, energy efficiency upgrades, supplier risk scoring, monthly compliance checks), and uses regular risk reviews with cross-functional representation to track indicators (lead times, on-time delivery, energy use per unit, and compliance incidents). When disruptions occur, contingency plans are activated and customer communications remain transparent, preserving service levels and revenue. |
| Measuring success |
|
Summary
Risk management in business is a foundational capability that protects assets, profits, and reputation while enabling strategic growth. By identifying risks early, assessing them accurately, and applying disciplined risk responses, organizations can prosper even in uncertain environments. The most successful programs integrate risk thinking into planning, operations, and governance, empowering leaders to make informed decisions, preserve value, and adapt with confidence through changing markets. A strong program fosters a proactive risk culture, clear ownership, measurable controls, and ongoing learning that collectively strengthen resilience and create sustainable value for customers, employees, and shareholders.